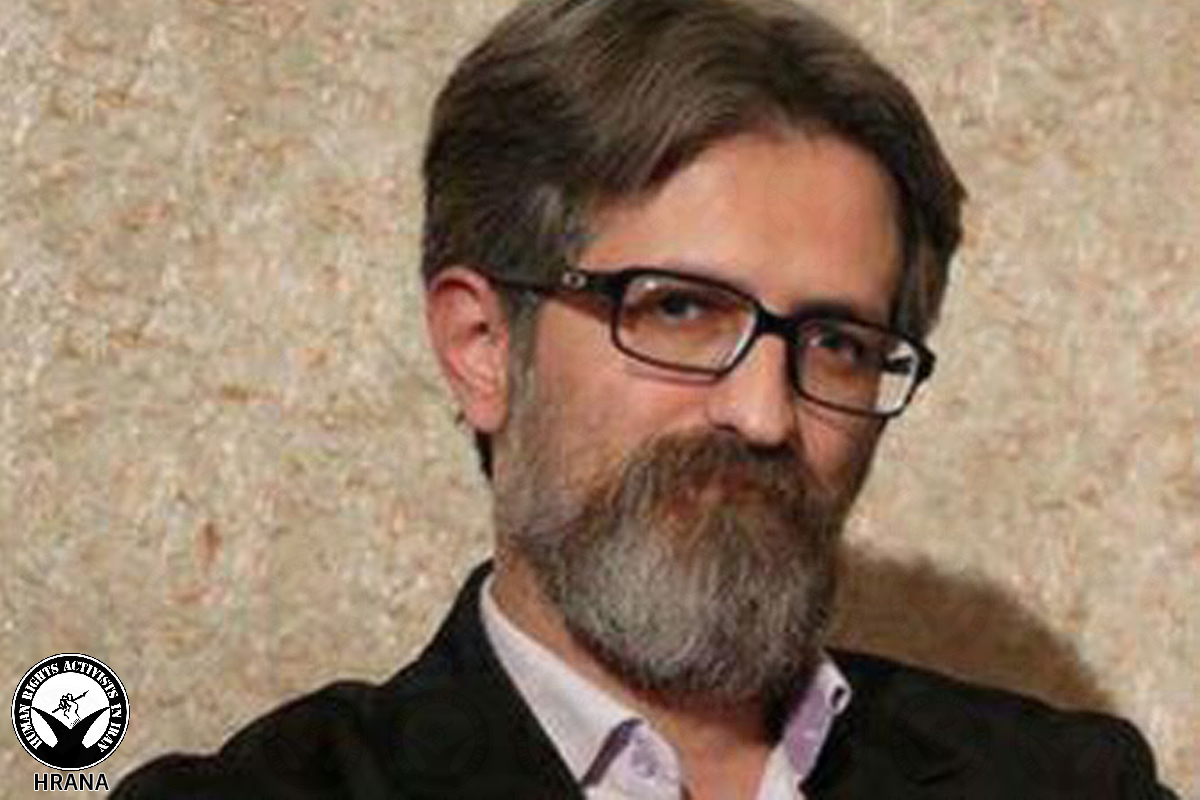
Human Rights Activists News Agency (HRANA) – Mostafa Daneshjoo, an attorney, is currently serving prison time for his legal advocacy and defense of the Gonabadi Dervishes, a religious minority. These days, Daneshjoo is sacrificing more than his freedom: he is now being forced to sacrifice his health.
Daneshjoo, despite suffering from acute lung and heart disease, has been barred access to medical attention of any kind since he was arrested on July 7, 2018.
According to Majzooban Noor, the Gonabadi Dervish Community News Website, when Daneshjoo was first detained, his family was cut off from contact with him for months. When they were finally permitted to see him in Ward 4 of Evin Prison, their relief was mingled with shock at the sight of his severely declining health.
Mostafa Daneshjoo is the former managing director of the Majzooban Noor website. While the clinic at Evin Prison has Daneshjoo’s medical file on hand, authorities–citing Daneshjoo’s prior arrest–are preventing him from seeking help, even from the generalists at the Evin Prison Clinic.
Daneshjoo was arrested in his mother’s home by seven armed officers in the early morning of July 7th. After spending 45 days in solitary confinement in Ward 209 of the Ministry of Intelligence detention center, he was transferred to Evin’s Quarantine Ward before being taken to Ward 4, typically reserved for prisoners with financial charges. Daneshjoo, who is asthmatic, experienced a sharp increase in symptoms after spending 45 days in a solitary cell without ventilation. While he was taken to Taleqani Hospital on July 21st, he was turned away without receiving care within a few hours.
Daneshjoo’s case file indicates that his current arrest warrant was issued by Branch 3 of the Shahid Moghaddas Prosecutor’s Office in Evin Prison. In a phone conversation at the time, he explained he was being pursued by authorities for his affiliation with the Dervishes who were involved in the Golestan Haftom incident. Authorities have reportedly wielded further punitive measures against him, according to a letter published in May 2017 by the Azad University Security Office, which announced that Daneshjoo was being prevented from pursuing his graduate studies in Penal Law and Criminology.
During prior defense proceedings of a number of Gonabadi Dervishes, following punitive reports from Iranian security agencies, Daneshjoo’s licence to practice law was revoked. He was sentenced — along with other attorneys, Dervish advocates, and his Majzooban Noor co-managers– to imprisonment on charges of “Membership in the Dervish anti-security sect,” “Acting against national security,” “Propaganda against the regime,” and “Disrupting public opinion.” Between 2011 and 2015, he served his sentence in Ward 350 of Evin Prison and was released in May 2015.








 HRANA News Agency – Prominent Iranian human rights lawyer, Mohammad Ali Dadkhah, was transferred to Ward 350 of Evin Prison in order to begin serving his 9 year prison sentence.
HRANA News Agency – Prominent Iranian human rights lawyer, Mohammad Ali Dadkhah, was transferred to Ward 350 of Evin Prison in order to begin serving his 9 year prison sentence.