Human Rights Activist News Agency (HRANA) – The following is an overview of human rights violations in Iran between September 23rd and October 22, 2018, per information compiled and verified by the Statistics, Publications, and Achievements Division of Human Rights Activists in Iran (HRAI).
Domestic restrictions in Iran on independent human rights reporting make it difficult to capture the full extent of these issues on the ground. The following overview draws on the work of HRANA reporters, as well as a network of independent and verifiable sources, including other human rights associations operating outside Iran’s borders.
Summary
Human rights violations continued all across the country over the past month, and included, but were not limited to: executions, child abuse, mass arrests, violation of prisoners’ rights, violation of freedom of expression, labor abuses, and unchecked environmental pollution.
Death Penalty
Capital punishment remains the most egregious violation of human rights in Iran. On October 10th — the World Day against the Death Penalty — the Center of Statistics at HRAI published its annual report to sensitize the public about the situation of the death penalty in Iran. The report provides statistics about executions carried out in this country between October 10, 2017, and October 9, 2018.
More than 25 citizens, including a juvenile offender, were executed in the last month (between September 23rd and October 22, 2018). More than 20 individuals, including a juvenile offender, were sentenced to death. Four people were executed in public.
HRANA was able to identify or gather details about death row prisoners, including a former member of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Arsalan Khodkam, the ex-spouse of Leila Tajik, Hedayat Abdollahpour and three individuals convicted of financial crimes. New details on the executions of Zanyar Moradi, Loghman Moradi, and Ramin Hossein Panahi were also reported during this period.
Freedom of Thought and Expression
Freedoms of thought and expression were also widely restricted over the past 30 days.
Arrests: Arrestees in this category included a Shiraz city council member, Ahmad Alinejad and his wife, at least 20 residents of Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province, writer and Mashad resident Abbas Vahedian, Zahra Majd in Isfahan, and six individuals involved in the Freedom Movement of Iran, arrested in Nain (near Isfahan).
Convictions: Leila Mir-Ghaffari was sentenced to 2 years in prison, Ejlal Ghavami to 8 months, Hassan Abbasi to 35 months (five 7-months prison terms), an Arak resident to 1 year and 30 lashings, Hamidreza Amini to 11 years. Women who protested this past August were sentenced from 6 months to 1 year in prison, Mohammad Mahdavifar was sentenced to 4 years and 6 months, a dual-nationality defendant faces 8 years and 6 months in prison, Soheil Arabi faces 3 years in prison, 3 years in exile, and a fine; the prison sentence of Abdolreza Ghanbari was increased to 15 years, Alireza Moeinian was sentenced to 8 months in prison; a new 6-month sentence extended the prison term of Saeed Shirzad through 2020; six Arak residents arrested amid the January protests were collectively sentenced to a total of 6 years in prison and 444 lashings, and a group of political activists in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province were sentenced to exile and prison terms ranging from 8 to 18 years.
Eleven civil activists, including Mohammad Najafi, Ali Bagheri, and Abbas Safari were sentenced to 3 years in prison and 74 lashings. Behzad Ali Bakhshi, Mohammad Yaghoubi, Yousef Shirilard, Neda Yousefi, Davoud Rahimi, Massoud Ajlou and Mohammad Torabi were sentenced to 1 year in prison and 74 lashings, suspended over five years. Kian Sadeghi faces 3 years in prison and 74 lashings, suspended over five years. Morteza Nazari was sentenced to a total of 13 years in prison, 2 years of exile, and a fine; Zahra Zare Seraji, on the same convictions, to 8 years in prison and a fine. Their co-defendants Ali Kabirmehr and Ali Bazazadeh were both sentenced to 13 years in prison and exile.
Summons: Hamid Farrokhnezhad, Parastoo Salehi, a number of reformist political activists, Tehran city council member Kazem Imanzadeh, Hossein Ahmadi Niaz, and Mohammad Najafi were all summoned by courts and the Ministry of Intelligence.
Censorship: The weekly magazines “Nabze Bazaar” and “Paytakht Kohan,” as well as the website “EntekhabKhabar,” were convicted in press court. Courts also issued indictments for the Chief Executive Officers of “Shargh” and “Shahrvand” newspapers for their reporting on sexual tourism. The National Front of Iran was prevented from holding its Central Council meeting in Tehran, a journalist was beaten by Qazvin municipal agents, and a Kurdish student was barred from education, presumably for his political affiliations.
Prisoners’ Rights
Prisoners are rarely protected from cruel and unusual punishments, and their rights to proper nutrition, hygiene, and medical treatment are systematically violated. A few of these victims are detailed below by category of violation.
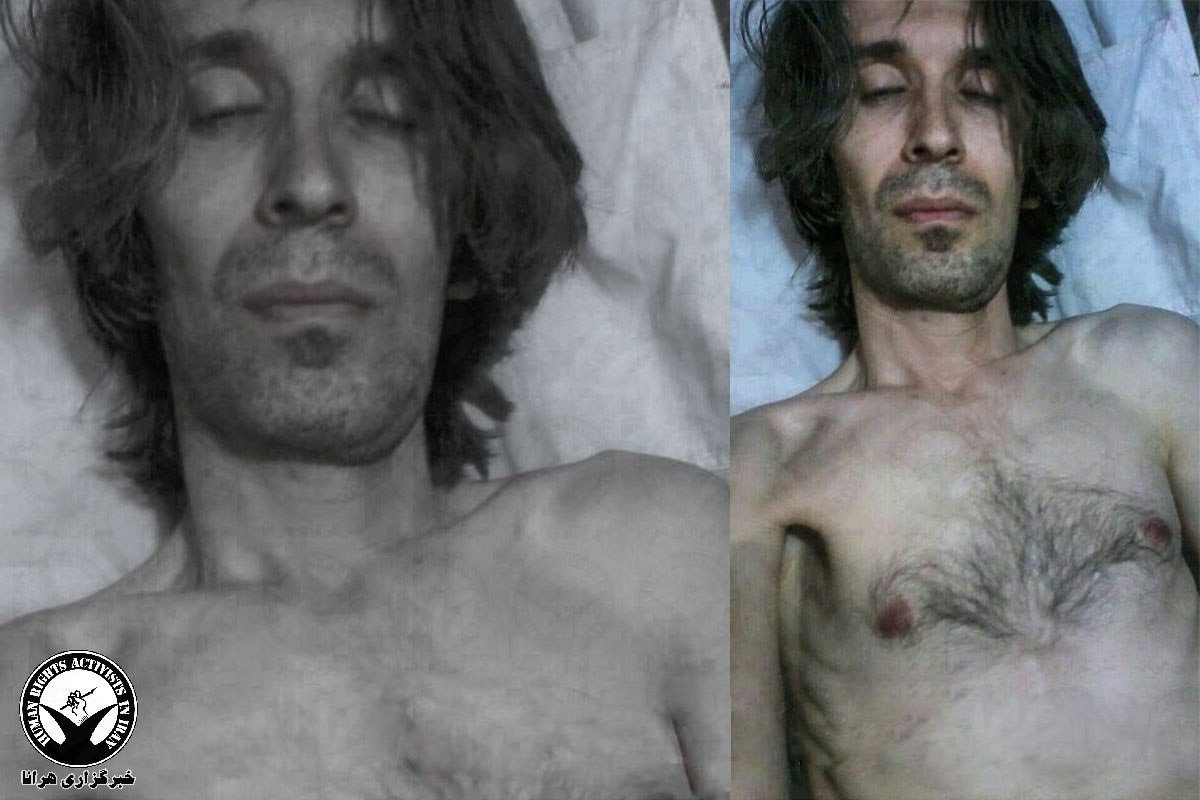
Raids and beatings: Prison agents punched Arash Sadeghi on his cancer surgery site; Urmia prison authorities attacked political prisoners and injured them severely, inciting them to hunger strike by the dozens; another Urmia prisoner was assaulted; a prisoner was beaten and injured by Rajai Shahr Prison personnel; Bandar Abbas Prison authorities broke an inmate’s fingers; an Urmia prisoner suffered a TBI after a beating by authorities; and prisoners were forcefully undressed and beaten in Zahedan Prison.
Withholding of medical treatment: A prisoner died after being denied medical care in Zahedan Prison. Farhad Meysami, Arash Sadeghi, and a prisoner in Sanandaj were also denied medical treatment.
Going without: Dozens of Gachsaran prisoners launched protests and hunger strikes in opposition to prison conditions. Six Gonabadi Dervish prisoners continued in an ongoing hunger strike. Reza Sigarchi, also in an act of protest, refused food and medicine in Great Tehran Penitentiary, while 8 Gonabadi Dervishes at the same penitentiary and 8 Baha’i prisoners of Karaj disappeared off of the administrative radar for 30 days. Houshmand Alipour was denied access to an attorney. Three prisoners in the Women’s Ward of Evin Prison were blocked from receiving visits, and the fate of sequestered labor activist and Sanandaj resident Zanyar Dabbaghian was still unknown.
Three prisoners attempted suicide in Zahedan, Urmia, and Saravan prisons. Local sources consistently impute prisoner suicides and suicide attempts to the violence and oppression of prison life.
Religious and Ethnic Minorities
Religious and ethnic minorities remained under threat and consistent judicial pressures this past month.
Baha’is: Eight Baha’i citizens were arrested in Baharestan (near Isfahan), four were arrested in Karaj, one of whom had his business forcibly shut down, and three were arrested in Shiraz.
[Some of these arrests reflect coordinated or group arrests, and linked articles will reflect that information overlap].
A Baha’i resident of Yazd who had been blocked from pursuing education was fired from work for their faith, and the parents of a Baha’i prisoner were temporarily detained following a search of the prisoner’s home.
Sunnis: Five Sunni scholars were sequestered for hours in the Zahedan-Khash road patrol office. Three Baluchi citizens, who are scholars of the Ghalamouei seminary, were arrested in Sirik County (southern Iran). Sunni scholars expressed outcry over the public statements of a soccer player they alleged to be disparaging of Sunni sanctities.
Six members of the Yamani Religious Group in Izeh County were also arrested, presumably for their beliefs.
Ethnic minorities: Arab citizens were arrested, and are still being arrested en masse in wake of the Ahvaz Parade Attack. HRANA is still in the process of confirming the identifies of the arrestees, which according to local reports number into the hundreds. Other arrests suspected to be ethnically discriminatory include Nasim Sadeghi, Mohammad Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, Mojtaba Parvin, Ebrahim Divazi, as well as residents of Ilam, Ahvaz, Marivan, Urmia, Sanandaj, Kermanshah, Saqqez, Pevah, Oshnavieh, and Sardasht.
News emerged on the convictions of Abbas Lasani, Kiumars Eslami, Eghbal Ahmadpour, Keyvan Olyali, Hossein Ali Mohammadi Alvar, as well as defendants in Sanandaj, Urmia, Kamyaran, and two detainees of the Afrin battles in Syria. Turkic activist Javad Ahmadi Yekanli was summoned by county security police in the city of Khoy.
Children’s Rights
Children are among the most vulnerable to human rights abuses in Iran. Over the past month, four wrongful child deaths were reported in the cities of Tehran, Falavarjan (Isfahan Province), Qaem Shahr (Mazandaran province) and (Isfahan Province).
The national director of Iran’s social emergency hotline said that 30% of reports called into the center are flagging some form of “domestic violence,” 30% of which turn out to be child abuse cases. Of this 30%, 50% were related to educational negligence, 30% to physical abuse, 15% to psychological abuse, and 4% to sexual abuse of children.
Maryam Sedighi, deputy director of the social welfare department of Alborz Province, said that 12% of “123” social emergency calls made in Alborz — i.e. an average of 40 calls per month — are child abuse reports.
Reports indicate the rape of a young girl by her father in Tehran; a boxing coach accused of raping his teenage student; a father pouring boiling water over his 7-year-old daughter in Genaveh, Bushehr Province; and a teacher using corporal punishment on a pupil in Kazeroon, Fars Province.
Three juvenile suicides were also reported: one student in Rigan County, Kerman Province, and two teenage girls, aged 14 and 16, in the cities of Abadan and Sanandaj.
The Iranian education system allocates fewer and fewer resources to its pupils, and educational facilities across the country — particularly in rural or underprivileged areas — can be found in varying states of wear and disrepair. One pupil in Razan, Hamadan province was injured in the chest, neck, and shoulders when he was caught in falling debris of a school wall that suddenly collapsed. The Razan director of education said that he is currently stable, but will require surgery.
Elementary-school student Donya Veisi of Garmash village, Kurdistan Province, fell victim to her own school’s disrepair when one of the walls surrounding her school yard collapsed, killing her. Later — amid allegations that Donya had in fact been raped and killed — the Kurdistan Prosecutor verbally engaged to investigate the matter.
Women
The question of women’s rights at sporting events gained heightened public attention this past month when, under pressure from FIFA to permit their entry into stadiums, a select number of Iranian women (most of them family members of players and federation employees) were finally allowed to witness a kickoff in person (Iran vs. Bolivia). Authorities’ exclusive selection criteria were highly criticized.
Meanwhile, Shiraz-based activist Maryam Azad was arrested by security forces at a Tehran Airport as she was leaving the country for Turkey.
The managing director of the office of forensic medicine in Kohkiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province indicated that, of the 429 domestic violence crimes recorded in his office over the past 6 months, 404 were incidents of violence by husbands against their wives.
Additional cases of violence against women included a man’s murder of his ex-wife when he failed to meet “mehrieh” obligations [a type of alimony settlement], and the circumstances surrounding one woman’s decision to set herself on fire in Mashad.
Two women, long hounded by the judiciary for participating in a rally on International Women’s Day, were recently acquitted of their charges.
Laborers and Guilds
This past month was rythmed by strikes, sit-ins, and rallies organized by guilds and employees across sectors who demanded more secure working conditions.
Commercial Transport: This past month, truck drivers in Iran went on a nationwide strike for the third time [in 12 months]. Over the course of their 20-day strike, at least 261 striking drivers in 19 different provinces were arrested and threatened with heavy sentences, including the death penalty. Strikers’ demands did make significant headway: after years of guild activism, the High Council of Transportation Coordination approved a new freight transport measurement rate known as the tonne-kilometre (tkm) method, which was among the most pressing demands of truck drivers. Despite this partial victory, the fates of the 261 detained protesters are still unknown.
Education: Six Educator-Activists who participated in demonstrations May 10th were sentenced to 9 months in prison and 74 lashings. Also reported was the conviction of schoolteacher and University of Tehran student Ruhollah Mardani, who was arrested earlier this year in connection to nationwide protests. Five teachers were summoned by the Bureau of Public Places in Saqqez.
Following a call to strike by the Coordinating Council of Teachers Syndicates in Iran (CCTSI), Iranian teachers staged sit-ins [on October 14th and 15th] to demand more liveable salaries and justice for their persecuted colleagues. Strike activity was recorded across the provinces of Kerman, Lorestan, Khuzestan, Kermanshah, Isfahan, Kurdistan, Alborz, Hamadan, Fars, Zanjan, Qom, Mazandaran, Tehran, North Khorasan, Ilam, East and West Azerbaijan, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, Bushehr, Gilan and Hormozgan.
Merchants: Merchants went on strike against the many interconnected symptoms of Iran’s current recession, including unstable exchange rates, inflation, rising prices, and unemployment. Merchant strikes went on for two consecutive days in the cities of Karaj, Shahreza, Shahriar, Shiraz, Kermanshah, Tabriz and Sarab.
Two street vendors were reportedly beaten by municipal agents in Qazvin and Gorgan.
Health and Environment:
Five environmental activists arrested 8 months ago have been indicted with charges of “corruption on earth,” which can carry the death penalty.
Intelligence agents halted a group of environmental journalists, including Javad Heydarian, before they could board a flight to Germany for work. Their passports were confiscated.
Public concern over pollution and waste issues is ballooning, and [many citizens are critical of the government’s inaction in face of myriad threats to the public health].
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Iranian Ministry of the Interior, Iranians surpass the worldwide average of daily waste production (300 grams) by a whopping 400 grams every day.
The head of the Environmental Protection Agency of Miandoab (West Azerbaijan Province) announced that contamination of the Zarrinehroud River from the city’s sugar factory, coupled with poor ecological management of the river and its dam system, has caused thousands of fish to die in the river.
High levels of air pollution were reported this month in the cities of Kerman, Mahshahr, Ramshir, Rigan, and the provinces of Sistan and Baluchestan and Kerman.
Cultural Rights and Censorship
A number of photographers from Shiraz faced persecution for their instagram activity this month [which was cited as “improper”].
Two cultural directors from Sistan and Baluchestan province were summoned to the Intelligence office for attempting to host a peaceful community celebration.
Pending content modifications and the resolution of charges against the Home Video Entertainment Network, the Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance banned distribution of the network’s TV series “13 Shomali” (Northern 13), which previously aired on Saturdays.
Military and Law-Enforcement Power Abuses
Several citizens were killed as a result of power abuses and negligence by security forces this past month.
Police car chases, inappropriate shootings by border authorities, and authorities’ failure to warn civilians of road barriers led to 2 civilian injuries and 5 civilian deaths in Iranshahr (Sistan and Baluchestan Province), Jask (Hormozgan Province) and Azadshahr (Golestan Province) and Razavi Khorasan.
Security forces reportedly assaulted fuel vendors in Saravan (Sistan and Baluchestan Province).
More than a dozen “Kulbars” [laborers who make their living carrying goods across border areas] were wounded and killed across the country, namely in Sardasht (West Azerbaijan Province), Piranshahr (West Azarbaijan Province), Urmia (West Azerbaijan Province) Nowsud (Kermanshah Province), Marivan and Baneh (Kurdistan Province) and Ilam (Ilam province).
A prisoner in Urmia was sentenced to hand amputation, and a robbery convict was dealt 74 lashes in public in the Zeberkhan Rural District (Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan Province).
__________________________________________________________________________
The above-cited reports are only a few examples of dismally more widespread trends. Their mention in this overview by no means implies their significance over those incidents which went unreported, due to tight restrictions on investigative journalists on the ground.
Among available reports of human rights abuses, however, some are more oft-cited due to their sensitive nature or predominating presence in public opinion. It bears mention that all human rights abuses are worthy of the news coverage and social media activism that has come to the aid of so relatively few. Bearing in mind their roles as public opinion influencers, social media activists and human rights reporters must be wary not to underlie existing human rights abuses with unintentional discrimination in their reporting.