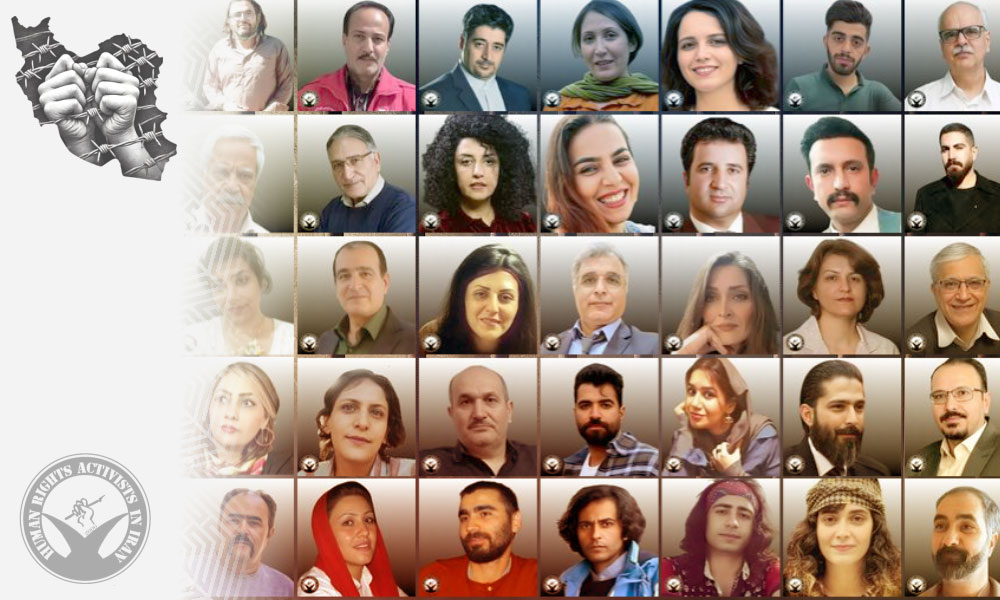
HRANA News Agency –Human Rights Day is an opportunity to reflect on the condition of imprisoned civil activists in Iran, individuals who are behind bars solely for defending fundamental human rights. HRANA, by publishing a list of these brave activists, calls on the international community to amplify their voices and demand the immediate release of advocates for freedom and justice.
This day serves as a moment to reconsider the role of human rights defenders and civil activists in societies where fundamental rights are still subject to structural violations. Marked annually on the global calendar, it commemorates the principles laid out in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted on December 10, 1948, principles that recognize freedom of expression, the prohibition of torture, the right to a fair trial, and human dignity as inalienable rights of all individuals. Nevertheless, the current reality in Iran highlights a stark gap between these international standards and the domestic situation.
In Iran, many human rights defenders, civil society activists, trade unionists, environmentalists, and advocates for fundamental freedoms face the threat of arrest, harsh sentences, and long-term deprivation, even for entirely peaceful activities conducted within the framework of domestic laws. These individuals, who constitute a significant part of the country’s civil society fabric, consistently encounter security pressures, broad restrictions, and systematic rights violations in their pursuit of transparency, justice, and equality. Most have been sentenced following closed-door trials, with limited access to legal counsel and based on vague or unsubstantiated charges, a process that not only contradicts Iran’s international obligations but also deeply impacts the civic space in the country.
In this report, HRANA publishes a list of over 61 imprisoned human rights defenders and civil activists in Iran, including 8 of whom currently being held in pretrial detention. This list is the result of ongoing collection, verification, and documentation efforts, aiming to provide a clear representation of the various dimensions of human rights violations against these defenders. The publication of this list is not merely the release of names; it tells a part of the story of Iranian civil society, in which the struggle to defend human rights can come at the cost of one’s freedom, health, and personal security.
Beyond commemorating foundational principles, Human Rights Day is also an occasion to consider the role of society and international institutions in supporting these defenders. Raising public awareness, demanding accountability from authorities, and supporting activists’ efforts are essential tools for advancing human rights in Iran. Through this report.
This report, in addition to documenting and reporting on these individuals’ conditions, is a step toward transparent and continuous documentation, aimed at preserving the truth, preventing collective amnesia, and laying the groundwork for accountability. Despite pressures and restrictions, human rights defenders in Iran remain a vital part of the collective effort to achieve a freer and more just society. Human Rights Day is a moment to once again bring their names and efforts to the forefront.
List of names:
 | 1. Mohammad Najafi, Civil Rights Activist Charges: Sending a voice message from Arak Prison and expressing support for the 2022 nationwide protests; spreading falsehoods; propaganda against the regime; insulting the Supreme Leader. Conviction: At least six separate cases totaling more than 24 years in prison. Place of imprisonment: Evin Prison. | |
 | 2. Sharifeh Mohammadi, labor activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime; acting against national security; baghi (armed rebellion) through membership in one of the opposition groups. | |
 | 3. Fatemeh Sepehri, civil activist Charges: Cooperation with hostile governments; assembly and collusion; insulting the Supreme Leader; propaganda against the regime; spreading falsehoods and disturbing public opinion. | |
 | 4. Golrokh Iraee, civil activist Charges: Assembly and collusion against national security; propaganda against the regime; disrupting public order. | |
 | 5. Maryam Akbari Monfared, civil activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and assembly and collusion against national security. | |
 | 6. Zartosht Ahmadi Ragheb, civil activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime; assembly and collusion to commit crimes against internal and external security. | |
 | 7- Payam Vali, Baha’i civil activist Charges: Cooperation with hostile governments; inciting or persuading people to war and killing each other; propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 8. Mohammad Davari, labor activist Charges: Insulting the Supreme Leader and propaganda against the regime in favor of anti-regime groups on the Internet. | |
 | 9. Hashem Khastar, civil activist Charges: Insulting the founder of the Islamic Republic; insulting sacred values; insulting the Supreme Leader; disturbing public opinion; cooperation with foreign media; participating in unlawful gatherings; and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 10. Anisha Asadollahi, labor activist Charges: Assembly and collusion against national security and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 11- Mehran Raoof, labor activist Charges: Participation in running an unlawful group and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 12- Mohammad Nourizad, civil activist Charges: Sending an audio file out of Evin Prison; disrupting public order; spreading falsehoods; insulting the founder of the Islamic Republic; insulting sacred values; insulting the Supreme Leader; disturbing public opinion; cooperation with foreign media; participating in unlawful gatherings; propaganda against the regime; and damaging the door and window of the ward chief’s office. | |
 | 13- Saeed Madani, civil activist Charges: Forming and administering anti-regime groups. | |
 | 14. Ahmadreza Haeri, civil activist Charges: Assembly and collusion with the intent to commit a crime against national security; propaganda activities against the regime; and spreading falsehoods. | |
 | 15. Reza (Gholamreza) Aghdasi, labor activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and assembly and collusion with the intent to commit a crime against national security. | |
 | 16. Arman Shadivand, environmental activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and insulting the Supreme Leader. | |
 | 17. Narges Mansouri, civil activist Charges: Assembly and collusion against national security, and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 18. Abbas Vahedian Shahroudi, civil activist Charges: Forming a group with the intent to act against national security, and cooperating with groups opposing the regime. | |
 | 19. Mohammad Abolhasani, civil activist Charges: Disrupting public order; assembly and collusion against national security; and propaganda activities against the regime. | |
 | 20- Taher Naghavi, attorney and civil activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 21- Maryam Jalal Hosseini, civil activist Charges: Inciting and persuading people to war and violence against one another with the intent to disrupt national security; propaganda against the regime; insulting the Supreme Leader; and forming a group aimed at undermining national security. | |
 | 22- Shakila Monfared, civil activist Charges: Membership in anti-regime groups; destruction of public property; disrupting public order and public peace; propaganda activities against the regime; and insulting Islamic sacred values. | |
 | 23- Morteza Seydi, labor activist Charges: Forming a group under the name of a labor union with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 24. Nasrollah Amirloo, labor activist Charges: Forming a group under the name of a labor union with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 25. Morteza Parvin, Azerbaijani-Turk activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 26. Foad Fathi, labor activist Charges: Membership in anti-regime groups; acting against national security; and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 27. Abdolrasoul Mortazavi, civil activist Charges: Insulting the founder of the Islamic Republic; insulting sacred values; insulting the Supreme Leader; disturbing public opinion; cooperating with foreign media; participating in unlawful gatherings; propaganda against the regime; and disrupting public order. | |
 | 28. Fariba Kamalabadi, Baha’i civil activist Charges: Administering an organization described by authorities as a “deviant and misguided sect” with the aim of disrupting national security. | |
 | 29. Javad La’al-Mohammadi, civil activist Charges: Giving interviews to foreign media and membership in anti-regime groups. | |
 | 30- Golareh Abbasi, civil activist Charges: Assembly and collusion against national security, and propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 31. Arsham Rezaei, civil activist Charges: Assembly and collusion with the intent to commit a crime against national security; propaganda activities against the regime; inciting people to clashes and bloodshed; acquiring illicit gains; and spreading falsehoods. | |
 | 32- Vadood Asadi, Azerbaijani-Turk activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime; membership in opposition groups; insulting the Supreme Leader; and assembly and collusion against national security. | |
 | 33- Salar Taher Afshar, Azerbaijani-Turk activist Charges: Assembly and collusion against national security. | |
 | 34. Abdolaziz Azimi-Ghadim, Azerbaijani-Turk activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and assembly, and collusion against national security. | |
 | 35. Elham Salehi, civil activist Charges: Propaganda activities against the regime; spreading falsehoods; and appearing in public without a hijab. | |
 | 36. Abolfazl Khoran, teachers’ union activist Charges: Insulting sacred values and disrupting public order and public peace. | |
 | 37- Masoud Farhikhteh, teachers’ union activist Charges: Assembly and collusion with the intent to commit crimes against the country’s internal security, and propaganda activities against the regime. | |
 | 38- Reza Mohammad-Hosseini, civil activist Charges: Membership in anti-regime groups with the aim of disrupting national security; assembly and collusion to commit a crime against national security; and propaganda activities against the regime. | |
 | 39- Mahboobeh Rezaei, civil activist Charges: Membership in anti-regime groups with the aim of disrupting national security; assembly and collusion with the intent to commit a crime against national security; propaganda activities against the regime; insulting Islamic sacred values; unveiling (appearing without hijab); and displaying immoral behavior in cyberspace. | |
 | 40. Abbas Lessani, Azerbaijani-Turk activist Charges: Forming an unlawful group; assembly and collusion against national security; and disrupting public order. | |
 | 41. Farhad Fahandej, Baha’i civil activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Fahandej. | |
 | 42. Jahangir Rostami, teachers’ union activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Rostami. | |
 | 43. Ehsan Rostami, cultural activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Rostami. | |
 | 44. Hassan Tozandehjani, cultural activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Tozandehjani. | |
 | 45. Ramin Rostami, cultural activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Rostami. | |
 | 46. Nima Mahdizadegan, cultural activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Mahdizadegan. | |
 | 47. Mehdi Farrahi Shandiz, teachers’ union activist Charges: No information has yet been made available regarding the charges brought against Mr. Farrahi Shandiz. | |
The following list includes activists who are currently outside prison due to a suspension of their sentences, furlough, or other similar circumstances: |
| |
 | 1. Narges Mohammadi, Nobel Peace Prize laureate and human rights activist Charges: Propaganda activities against the Islamic Republic of Iran through publishing a statement (the statement against executions); staging a sit-in inside the prison office; disobeying the prison warden and officials (for refusing to end the protest sit-in); breaking windows; defamation and causing bodily harm; confrontation with an officer and disobedience; and additional propaganda activities against the regime. | |
 | 2- Amirsalar Davoudi, attorney and human rights activist Charges: Insulting the Supreme Leader; disturbing public opinion; and forming an anti-security group. | |
 | 3- Fatemeh (Mojgan) Tadrisi, civil activist Charges: Inciting and persuading people to war and violence against one another with the intent to disrupt national security; propaganda against the regime; insulting the Supreme Leader; and forming a group aimed at undermining national security. | |
 | 4. Peyman Farhangian, labor activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime and forming a group with the intent to disrupt public order. | |
 | 5. Jelveh Javaheri, women’s rights activist Charges: Propaganda against the regime. | |
 | 6. Yasamin Heshdari, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 7- Sara Jahani, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 8- Matin Yazdani, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 9- Negin Rezaei, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 10- Forough Sami-Nia, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 11- Shiva Shah-Siah, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 12- Azadeh Chavoshian, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 13- Zohreh (Fatemeh) Dadras, women’s rights activist Charges: Forming a group with the aim of disrupting national security, and assembly and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
 | 14. Zahra Dadras, women’s rights activist Charges: Membership in a group and assembly, and collusion with the intent to disrupt national security. | |
Human Rights Day is also an opportunity to re-examine the values that form the foundation of human dignity, values such as justice, freedom, and equality, rooted in international documents and human experience. The names recorded in this report reflect only a portion of a broader reality, one in which human rights defenders and civil activists in Iran, solely for their commitment to human principles and peaceful activities, face deprivation of liberty, security pressures, and fundamental rights violations.
These individuals, despite the limitations and high costs, embody values recognized by the international community. Silence or indifference toward their condition is not only a disregard for human suffering but also a dismissal of the principles on which the international system is built. In this context, on Human Rights Day, the following are demanded from Iranian authorities and the international community:
• Immediately and unconditionally release all individuals detained for the peaceful exercise of their rights, and review all related convictions to vacate unjust charges and ensure reparations for victims.
• End unlawful restrictions on the freedom of expression, association, assembly, and civic engagement, and halt the use of vague national security charges that criminalize peaceful dissent.
• Guarantee due process and fair trial rights, including access to independent legal counsel from the moment of arrest, transparent legal proceedings, and full access to families, medical care, and communication.
• Prohibit torture and all forms of ill-treatment, end the use of coerced forced confessions, and allow independent monitoring and inspections of all detention facilities.
• Allow independent monitoring and international engagement, including granting access to the UN Fact-Finding Mission, Special Rapporteurs (Thematic and Geographic Mandates), and credible civil society organizations to assess conditions and investigate violations.
• Establish effective accountability and oversight mechanisms to prevent recurrence of abuses, ensure judicial independence, reform vague criminal provisions enabling arbitrary detention, and hold perpetrators who enable the cycle of abuse against activists, responsible.
Finally, civil society as well as citizens across the globe are called upon to continue their support, advocacy, and awareness-raising efforts, ensuring that the situation of these prisoners is not sidelined. Amplifying their voices and demanding adherence to human rights obligations are essential steps toward achieving lasting change and alleviating the suffering of those who have sacrificed their freedom in defense of human rights.